What is an Endocrinologist?
An endocrinologist is a medical doctor who specializes in the diagnosis and treatment of health conditions related to hormonal imbalances and disorders of the endocrine system.
The endocrine system comprises various glands and tissues that produce hormones, which are vital chemical messengers in the body. These hormones regulate numerous physiological processes, including metabolism, growth and development, reproduction, and mood.
Endocrinologists undergo extensive training to develop a thorough understanding of how hormones affect the body’s functions.
They diagnose, treat, and manage conditions stemming from hormone imbalances, providing personalized care based on the specific needs of their patients. Common disorders managed by endocrinologists include:
Diabetes: A chronic condition characterized by high blood sugar levels due to insulin resistance or insufficient insulin production.
Thyroid Disorders: Conditions affecting the thyroid gland, including hypothyroidism (underactive thyroid) and hyperthyroidism (overactive thyroid).
Hormonal Imbalances: Issues such as polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS) or low testosterone levels in men.
Metabolic Disorders: Conditions that disrupt normal metabolism, such as obesity or metabolic syndrome.
Bone Health: Management of osteoporosis and related conditions.
Endocrine Tumors: Certain cancers that affect hormone-producing glands.
Hormone therapy is often used as a treatment option for conditions like PCOS, infertility, and low testosterone in men.
Types of Endocrinologists
Endocrinologists can specialize in different areas of endocrinology, which can impact their approach to treatment. Common specializations include:
Pediatric Endocrinology: Focuses on hormone-related conditions in children, such as growth disorders and puberty issues.
Geriatric Endocrinology: Deals with hormonal changes and challenges faced by older adults, focusing on conditions like osteoporosis and diabetes management.
Reproductive Endocrinology: Concentrates on hormonal issues related to fertility, menstruation, and menopause.
Metabolic Disorders: Specializes in conditions related to metabolism, obesity, and diabetes.
Some endocrinologists also engage in research or teach in academic settings, while others work in private practices or hospital settings.
The Endocrine System and Its Hormones
The endocrine system is a complex network of glands that secrete hormones directly into the bloodstream. Hormones regulate various bodily functions, and understanding this system is crucial for identifying and managing hormone-related disorders. Key glands in the endocrine system include:
Pituitary Gland: Often referred to as the “master gland,” it regulates other endocrine glands and is critical in growth and metabolism.
Thyroid Gland: Produces hormones that regulate metabolism, energy levels, and growth.
Adrenal Glands: Produce hormones such as cortisol and adrenaline, which help manage stress and metabolism.
Pancreas: Plays a vital role in blood sugar regulation by producing insulin and glucagon.
Ovaries and Testes: Produce sex hormones (estrogen, progesterone, and testosterone) that affect reproduction and secondary sexual characteristics.
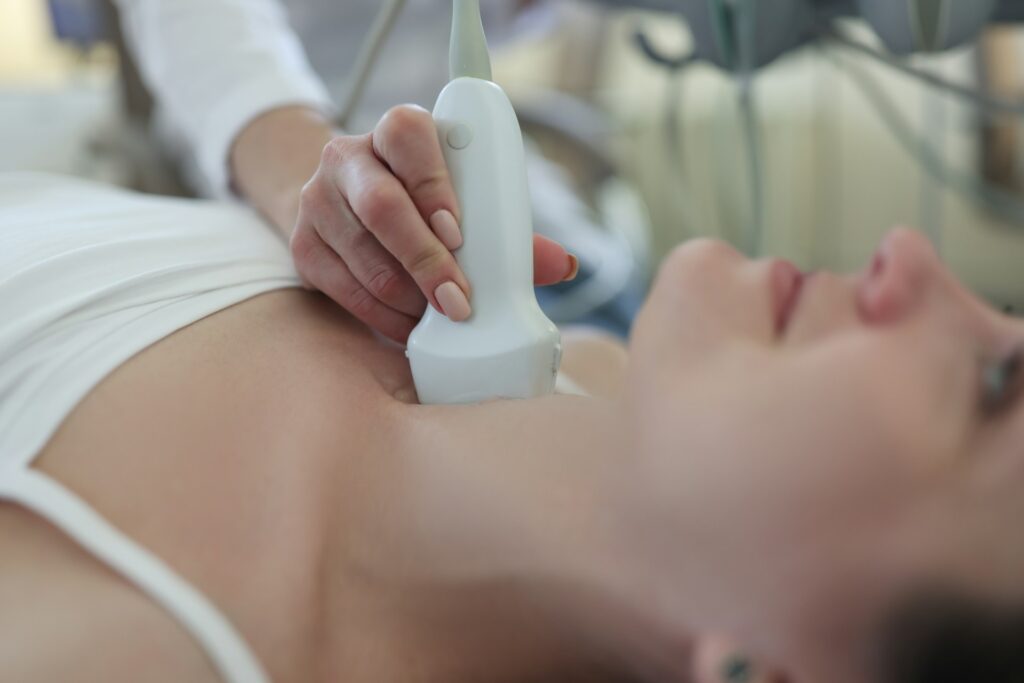
Endocrine Glands and Hormones
The endocrine system is a complex network of glands and organs that produce and regulate hormones in the body.
Hormones are chemical messengers that travel through the bloodstream to reach their target cells, where they play a crucial role in controlling various bodily functions, such as growth, metabolism, reproduction, and development.
Key glands in the endocrine system include:
Pituitary Gland: Often referred to as the “master gland,” it regulates other endocrine glands and is critical in growth and metabolism.
Thyroid Gland: Produces thyroid hormones that regulate metabolism, energy levels, and growth. An enlarged thyroid gland can indicate thyroid disease or thyroid disorder.
Adrenal Glands: Produce hormones such as cortisol and adrenaline, which help manage stress and metabolism.
Pancreas: Plays a vital role in blood sugar regulation by producing insulin and glucagon.
Ovaries and Testes: Produce sex hormones (estrogen, progesterone, and testosterone) that affect reproduction and secondary sexual characteristics.
Pineal Gland: Produces melatonin, which regulates sleep-wake cycles.
Parathyroid Glands: Regulate calcium levels in the blood, which is crucial for bone health and muscle function.
Understanding the function of these endocrine glands and the hormones they produce is essential for identifying and managing hormonal imbalances and endocrine disorders.
Hormone imbalances can lead to a variety of health issues, making it important to seek medical advice if you experience symptoms related to these glands.
By recognizing the signs of hormonal imbalances and understanding the role of the endocrine system, you can take proactive steps to maintain your hormonal health and overall well-being.
Hormonal Disorders Treated by Endocrinologists
Endocrinologists manage a variety of conditions related to hormonal imbalances, including but not limited to:
Diabetes Management: Both Type 1 and Type 2 diabetes require careful monitoring and treatment.
Thyroid Disorders: Hypothyroidism, hyperthyroidism, and thyroid nodules are common issues addressed by endocrinologists.
Adrenal Disorders: Conditions like Cushing’s syndrome or Addison’s disease can significantly impact health and require specialized care.
Polycystic Ovary Syndrome (PCOS): A hormonal disorder affecting women that can cause irregular periods, weight gain, and infertility.
Low Testosterone: Men with low testosterone levels can experience various symptoms, including reduced libido and fatigue.
Hormonal Disorders: Endocrinologists diagnose and treat various hormonal imbalances affecting overall health.
In cases of hormone deficiency, synthetic growth hormone may be administered through injections to normalize hormone levels.

The Training and Expertise of Endocrinologists
To become an endocrinologist, one must complete a rigorous educational pathway, including:
Medical School: This typically involves four years of medical training.
Internal Medicine Residency: Following medical school, candidates complete a residency program in internal medicine, usually lasting three years.
Endocrinology Fellowship: After completing their residency, doctors pursue a fellowship in endocrinology, which typically lasts another two to three years, focusing on the endocrine system and related disorders.
Endocrinologists are required to stay current with the latest research and treatments through continuing medical education (CME) courses. Many choose to obtain board certification in endocrinology, which requires passing a comprehensive exam.
Why See an Endocrinologist for Thyroid Disease?
Consulting an endocrinologist is beneficial for anyone experiencing symptoms related to hormonal imbalances or endocrine disorders. You might consider seeing an endocrinologist if you experience:
Unexplained weight gain or loss.
Persistent fatigue or changes in energy levels.
Menstrual irregularities or fertility issues.
Symptoms of diabetes, such as excessive thirst or frequent urination.
Signs of thyroid dysfunction, like changes in weight, mood, or temperature sensitivity.
Endocrinologists provide specialized knowledge and can develop individualized treatment plans that may be more effective than standard primary care approaches.
What to Expect When Visiting an Endocrinologist
Your first appointment with an endocrinologist typically involves a comprehensive evaluation, including:
Medical History: Be prepared to discuss your medical history, family history, and any current medications.
Physical Examination: The endocrinologist may perform a physical exam to assess symptoms.
Diagnostic Testing: Blood tests or imaging studies may be ordered to evaluate hormone levels and assess gland function.
After your evaluation, the endocrinologist will discuss their findings and work with you to develop a personalized treatment plan.
Choosing the Right Endocrinologist
When selecting an endocrinologist, consider the following factors:
Board Certification: Ensure the endocrinologist is board-certified in endocrinology.
Experience: Look for someone who has experience treating your specific condition.
Reputation: Read reviews and ask for recommendations from friends or family.
Communication Style: Choose a doctor who communicates well and makes you feel comfortable discussing your health.

Frequently Asked Questions
What are hormone doctors called?
Hormone doctors are typically called endocrinologists.
Which doctor is best for hormonal imbalance?
An endocrinologist specializes in diagnosing and treating hormonal imbalances.
How do I get my hormones checked?
You can consult a healthcare provider who can order blood tests to assess hormone levels.
Can a gynecologist treat hormonal imbalance?
Yes, gynecologists often treat hormonal imbalances, especially those related to reproductive health.
Understanding Hormone Doctors Conclusion
Endocrinologists play a vital role in diagnosing and managing health conditions related to hormonal imbalances and endocrine disorders.
If you experience symptoms that suggest a hormone-related issue, don’t hesitate to seek the expertise of an endocrinologist.
By understanding the function of these specialists and knowing when to seek their help, you can take proactive steps toward managing your hormonal health effectively.


